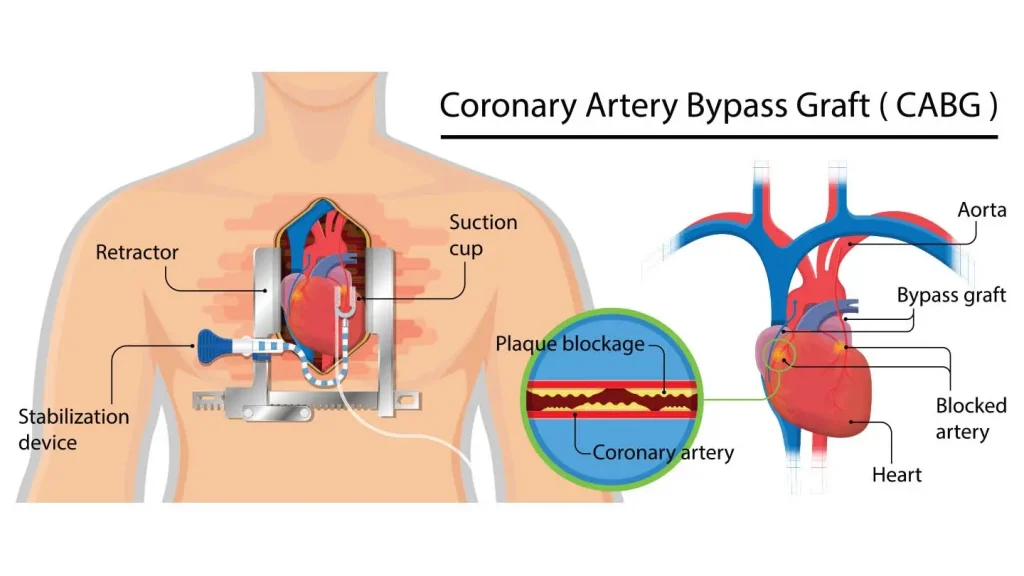
About CABG
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery is a procedure used to improve blood flow to the heart muscle by bypassing blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. During the surgery, a surgeon takes a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body, such as the chest, leg, or arm, and grafts it onto the coronary artery beyond the blocked area. This creates a new route for blood to flow to the heart, bypassing the blocked or narrowed section. CABG surgery is often performed to relieve chest pain (angina) and reduce the risk of heart attack.
Risks and precautions
CABG surgery, while often successful, carries risks like any major surgical procedure. These include bleeding, infection, stroke, and heart rhythm disturbances. Patients may also experience complications related to anesthesia and medications. To mitigate risks, patients are advised to inform their healthcare providers about any medications or supplements they’re taking and follow pre-surgery instructions closely. After surgery, patients should adhere to post-operative care guidelines, which may include medication regimens, lifestyle changes, and attending follow-up appointments. Despite the risks, CABG surgery can significantly improve heart health and quality of life for many individuals.