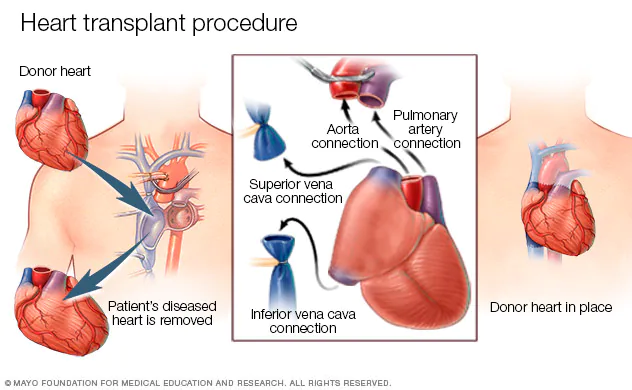
About Heart Transplant
Heart transplant surgery involves replacing a diseased or failing heart with a healthy heart from a deceased donor. It’s typically considered for patients with end-stage heart failure or other severe heart conditions that cannot be managed effectively with other treatments. During the surgery, the recipient’s diseased heart is removed, and the donor heart is connected to the recipient’s blood vessels and remaining heart structures. Strict adherence to post-transplant care, including medication regimens and lifestyle modifications, is essential for a successful outcome.
Risks and precautions
Heart transplant surgery carries several risks, including rejection of the donor heart, infection, bleeding, and complications from immunosuppressive medications. Rejection occurs when the recipient’s immune system recognizes the transplanted heart as foreign and attacks it. To mitigate this risk, patients must strictly adhere to their prescribed medication regimen, which typically includes immunosuppressants to suppress the immune system’s response. However, these medications also increase the risk of infections, so patients should take precautions to avoid exposure to infectious agents.
Bleeding is a potential complication during or after surgery, requiring close monitoring and intervention. Patients should avoid activities that could increase the risk of bleeding, such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercise, during the recovery period. They should also be vigilant for signs of bleeding, such as excessive bruising or bleeding from surgical incisions, and seek prompt medical attention if any occur.
In addition to the risks associated with surgery and medications, patients are also at risk of developing other complications, such as kidney problems and cardiovascular issues. To minimize these risks, patients should adhere to a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoidance of tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. They should also attend regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare providers for monitoring and adjustment of medications, as well as ongoing management of any comorbid conditions.
Overall, while heart transplant surgery offers the potential for improved quality of life and extended survival for patients with end-stage heart failure, it requires careful management and adherence to medical recommendations to minimize the risk of complications and optimize outcomes.